728x90
1. EDA 정의 (Event-Driven Architecture)
: 이벤트 기반 아키텍처는 시스템 내 컴포넌트들이 이벤트를 중심으로 상호작용하도록 설계된 아키텍처 패턴
1) 한 서비스가 상태 변화나 특정 행동을 이벤트로 발행(publish)
2) 다른 서비스는 그 이벤트를 구독(subscribe) 하여 필요한 작업 수행
3) 전체 패키지 구조를 정하는 다른 아키텍처와는 달리, EDA는 타 아키텍처 기반에서
강결합과 비동기 등의부족한 부분을 보완할 수 있는 개발 패턴 중 하나 임
목표: "서비스 간 결합도를 낮추고, 확장성과 비동기 처리를 쉽게 만드는 것"
2. 핵심 구성 요소

| 구성 요소 | 역할 |
| Event | 시스템에서 발생한 사건 또는 메시지 (ex: OrderCreated, UserRegistered) |
| Publisher | 이벤트를 발생시키는 컴포넌트 (Application Service 등) |
| Listener | 이벤트를 구독하고 처리하는 컴포넌트 |
| Event Broker | 이벤트를 전달/중계하는 시스템 (Kafka, RabbitMQ, Spring ApplicationEvent 등) |
3. 예제 코드
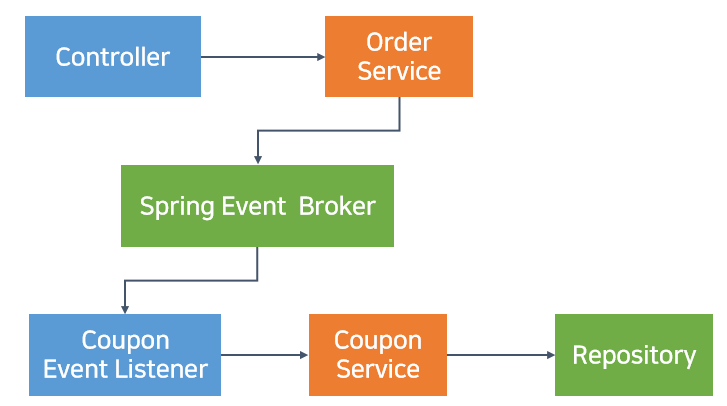
1) event 정의
package com.example.order.event
data class OrderCreatedEvent(
val orderId: Long,
val userId: Long,
val totalPrice: Double
)
2) Publisher
package com.example.order.application
import com.example.order.domain.Order
import com.example.order.domain.OrderRepository
import com.example.order.event.OrderCreatedEvent
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional
@Service
class OrderService(
private val orderRepository: OrderRepository,
private val eventPublisher: ApplicationEventPublisher //Spring 내장 이벤트 브로커
) {
@Transactional
fun createOrder(userId: Long, totalPrice: Double): Order {
val order = Order(userId = userId, totalPrice = totalPrice)
val savedOrder = orderRepository.save(order)
// 이벤트 발행(publisher)
eventPublisher.publishEvent(OrderCreatedEvent(savedOrder.id!!, userId, totalPrice))
return savedOrder
}
}
3. Event Listener (Consumer 역할)
package com.example.order.listener
import com.example.order.event.OrderCreatedEvent
import com.example.order.domain.CouponDomainService
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service
@Service
class CouponEventListener(
private val couponDomainService: CouponDomainService
) {
@EventListener
fun handleOrderCreated(event: OrderCreatedEvent) {
// 주문 이벤트를 받아서 쿠폰 발급
couponDomainService.issueCoupon(event.userId)
}
}
4. 장 & 단점
"느슨한 결합(Loose Coupling)"
- 서비스 간 직접 호출 대신 이벤트로 통신
- Publisher와 Consumer는 서로를 몰라도 됨
"비동기 처리 가능"
- 이벤트를 큐나 브로커에 발행 → 소비자가 처리
- 유스케이스 흐름이 느린 서비스에 영향을 주지 않음
"확장성"
- 새로운 기능 추가 시 이벤트 Listener만 추가하면 됨
- 기존 Publisher는 수정 불필요
"복잡성 증가"
- 이벤트 흐름 추적, 트랜잭션 관리, 디버깅이 어려움728x90
'Kotlin Spring > Kotlin Spring 강의 내용' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 7) 주요 기능 개발(Back-end) (0) | 2025.09.02 |
|---|---|
| 6) 개발 architecture (5) 강의용 Architecture (0) | 2025.09.01 |
| 6) 개발 architecture (3) 클린 아키텍처(Clean Architecture) (2) | 2025.08.31 |
| 6) 개발 architecture (2) 헥사고날 아키텍처(Hexagonal Architecture) (0) | 2025.08.31 |
| 6) 개발 architecture (1) 레이어드 아키텍처(Layered Architecture) (0) | 2025.08.31 |

